In our previous post, we delved into hypothyroidism, a prevalent thyroid disorder caused by an underactive thyroid gland. Today, we’re shifting our focus to another thyroid condition: hyperthyroidism in aging.
Imagine your thyroid gland as a tiny orchestra conductor, orchestrating the symphony of hormones in your body. Well, sometimes this conductor gets a little too enthusiastic, waving its baton with gusto. That’s when hyperthyroidism steps onto the stage.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when this gland goes into overdrive, cranking out thyroid hormones like a caffeinated barista on a Monday morning. The result? A metabolic rollercoaster that can leave you feeling like you’ve downed a triple espresso.
Hyperthyroidism in Aging: What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy and Active
You’re a seasoned traveler on the winding road of life, and suddenly, your thyroid decides to throw a wild party. Welcome to the world of hyperthyroidism—where your thyroid gland cranks up the volume like a rebellious teenager with a boombox.
So, what’s the deal with hyperthyroidism in our golden years?
Your thyroid gland, that tiny conductor in your neck, starts conducting like it’s at a rock concert. It pumps out more thyroid hormones than a caffeinated squirrel on a mission. Hyperthyroidism messes with your metabolism. Not to mention the problems to your bones and heart. Early detection helps you see these problems before they become serious.
Prefer to listen rather than read?
Causes and Risk Factors
Hyperthyroidism in aging is excessive thyroid hormone production. Many factors can lead to this problem. Let’s explore these causes and understand the associated risks:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder, Graves’ disease prompts the immune system to attack the thyroid gland. This assault leads to the overproduction of thyroid hormones, contributing to hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid Nodules: Abnormal growths or nodules on the thyroid gland can disrupt hormone regulation. Some nodules become hyperactive, releasing excess thyroid hormones.
- Thyroiditis: It is the inflammation of the thyroid gland, This condition may be temporary or chronic.

Aging and Hyperthyroidism
While aging itself isn’t a direct cause of hyperthyroidism, the natural aging process brings about hormonal changes. These shifts can render older individuals more vulnerable to developing thyroid disorders. Risks grow as you age.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Detecting hyperthyroidism in older adults can be tricky. Unlike younger individuals, older patients may exhibit subtle or atypical symptoms. This complexity underscores the importance of seeking professional evaluation if hyperthyroidism is suspected.
Considerations for Older Individuals
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you suspect hyperthyroidism in an aging individual, seek medical advice promptly. A healthcare provider can assess symptoms, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Coexisting health issues or medications commonly used by older adults can complicate the diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism. A comprehensive evaluation is crucial.
Remember, early detection of hyperthyroidism in aging and personalized care are essential for managing this problem effectively, especially in older populations.
Recognizing Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism in aging manifests as different symptoms. These signs differ from person to person. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely medical intervention. Common signs in aging individuals include:
Fatigue and Weakness
For seniors, hyperthyroidism can severely impact energy levels, leading to significant fatigue and weakness. These symptoms are debilitating and can prevent them from performing everyday tasks. Even simple chores may seem daunting as their bodies struggle to meet the demands of daily life.
It’s vital for seniors experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice promptly. Addressing these issues early can help them regain vitality and maintain an active lifestyle. Exploring treatment options with a healthcare provider is a key step toward managing their condition effectively.
Weight Loss
One clear sign of hyperthyroidism in aging individuals is unexpected weight loss. This happens even when their appetite stays the same or even increases. Despite not trying to lose weight, individuals and their families often notice a rapid decline in weight. Hyperthyrodism means less amount of calories used by the body.
The thyroid gland acts like a throttle, speeding up the body’s metabolic engine. This leads to nutrients breaking down faster and calories burning more rapidly, which results in weight loss. Do not think this way of weight loss is good.

For seniors experiencing unexplained weight loss, it’s crucial to consult a doctor. A timely diagnosis and proper treatment can restore balance and prevent further health issues caused by hyperthyroidism.
Rapid Heartbeat
Hyperthyroidism doesn’t just affect the thyroid; it impacts the entire body, including the heart. As people age, they may encounter a notable rise in heart rate. It is a phenomenon called tachycardia. This can manifest as a sensation of their heart pounding vigorously within their chest, accompanied by palpitations and a fluttering feeling.
These symptoms can be unsettling and may include irregular or forceful heartbeats, adding to the discomfort. Such disturbances in heart rhythm are not only alarming but can also be dangerous.

Recognizing that hyperthyroidism can severely affect the cardiovascular system underscores the importance of timely medical evaluation and treatment. Proper management of the condition helps stabilize the heart rate and brings a sense of calm and assurance back to seniors’ lives.
Heat Intolerance
Aging individuals battling hyperthyroidism in aging often find themselves grappling with an unwelcome companion: heightened sensitivity to heat.
In a cruel twist, even in perfectly comfortable temperatures, they may find themselves feeling uncomfortably hot and excessively sweaty. It’s as if their internal thermostat has gone haywire, leaving them at the mercy of relentless waves of warmth.
This intensified response to heat can be immensely frustrating and disruptive to their daily lives. What was once a cozy environment now feels suffocating, and the simple act of staying cool becomes a relentless pursuit.
Whether it’s seeking refuge in air-conditioned spaces, donning lightweight and breathable clothing, or employing ingenious cooling techniques, individuals with hyperthyroidism must adapt and find ways to keep their internal temperature in check.
By recognizing and addressing this unique symptom, they can navigate their way through the sweltering challenges of hyperthyroidism in aging and regain a sense of comfort in their surroundings.
Mood Changes
Hyperthyroidism in aging greatly affects your well-being, going beyond physical symptoms. Those with this condition often experience emotional distress due to the erratic influence of the thyroid gland on their mood and mental state.
Anxiety becomes a constant companion, creeping into their thoughts and causing a sense of unease that lingers throughout the day. Irritability takes hold, rendering even the most trivial matters sources of frustration and agitation.
Restlessness permeates their being, making it challenging to find respite or settle into a state of calm. Concentration becomes a strenuous task, as their minds dart from one fleeting thought to another, struggling to maintain focus amidst the tumultuous backdrop of hyperthyroidism in aging individuals.
This rollercoaster of emotions can be overwhelming, impacting their overall quality of life and relationships. Recognizing these emotional fluctuations as a symptom of hyperthyroidism in aging is crucial, as it highlights the need for comprehensive treatment that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
By finding the right balance, individuals can regain stability, serenity, and a sense of emotional well-being as they navigate the complexities of aging with hyperthyroidism.
Muscle Weakness
In the realm of hyperthyroidism in aging, weakness and trembling of the muscles emerge as formidable adversaries, particularly targeting the upper arms and thighs.
Aging individuals grappling with this condition often find themselves contending with a disconcerting loss of strength and an unsettling trembling sensation that reverberates through their limbs.
Everyday tasks that were once effortless now demand an extraordinary effort, as the muscles struggle to muster the necessary power. Simple activities like lifting objects or climbing stairs can become daunting challenges, overshadowed by the persistent weakness that threatens to impede their progress.
As if the physical frailty weren’t enough, the tremors add an additional layer of complexity, making even the most delicate actions feel unsteady and uncontrolled. The battle against muscle weakness and trembling becomes a quest for resilience and stability, necessitating a comprehensive approach to managing the underlying hyperthyroidism in aging.
By addressing the root cause, individuals can embark on a journey towards restoring strength to their weary muscles and reclaiming the freedom to move with confidence and grace.
Changes in Bowel Habit
For people grappling with hyperthyroidism in aging, the digestive system becomes an unwitting participant in the chaos unfolding within their bodies.

One of the notable gastrointestinal manifestations of this condition is the unwelcome arrival of frequent bowel movements or bouts of diarrhea. This sudden and uncontrollable urge to relieve the bowels can disrupt their daily routines and create a sense of unease and inconvenience. What was once a predictable and regular pattern now becomes unpredictable and erratic.
The increased activity within the digestive tract, triggered by the overactive thyroid gland, accelerates the transit time of food through the intestines, leaving a limited opportunity for proper absorption of nutrients and water. As a result, stools may become loose, watery, and more frequent than usual.
Constantly needing a restroom and fearing accidents can be distressing for aging people with hyperthyroidism. Recognizing that these digestive issues are linked to the condition is important for seeking medical help and finding ways to manage and reduce symptoms.
By regaining control over their digestive health, individuals can restore stability and harmony to their daily lives.
Eye Problems
Aging individuals navigating the complexities of hyperthyroidism in aging may find themselves grappling with a range of eye-related symptoms that can be both visually and physically distressing.
Another notable manifestation is the unsettling occurrence of bulging eyes, also known as exophthalmos. This protrusion of the eyes from their normal position can be a disconcerting sight, affecting not only one’s appearance but also their self-confidence.
Individuals with hyperthyroidism may have dry and irritated eyes due to excessive thyroid hormones. This can cause dryness, discomfort, and difficulty in daily activities that require visual focus.
Hyperthyroidism can cause double vision, impacting coordination and perception. Misalignment of the eyes leads to blurred or overlapping vision, making reading and driving challenging.
The severity of these symptoms can vary between individuals. It is important to understand that having one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean a person has hyperthyroidism. It is crucial to undergo a thorough medical evaluation and diagnosis to confirm the condition.
Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism in Aging Individuals
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism involves similar processes but with some key differences due to the opposite nature of the two conditions.
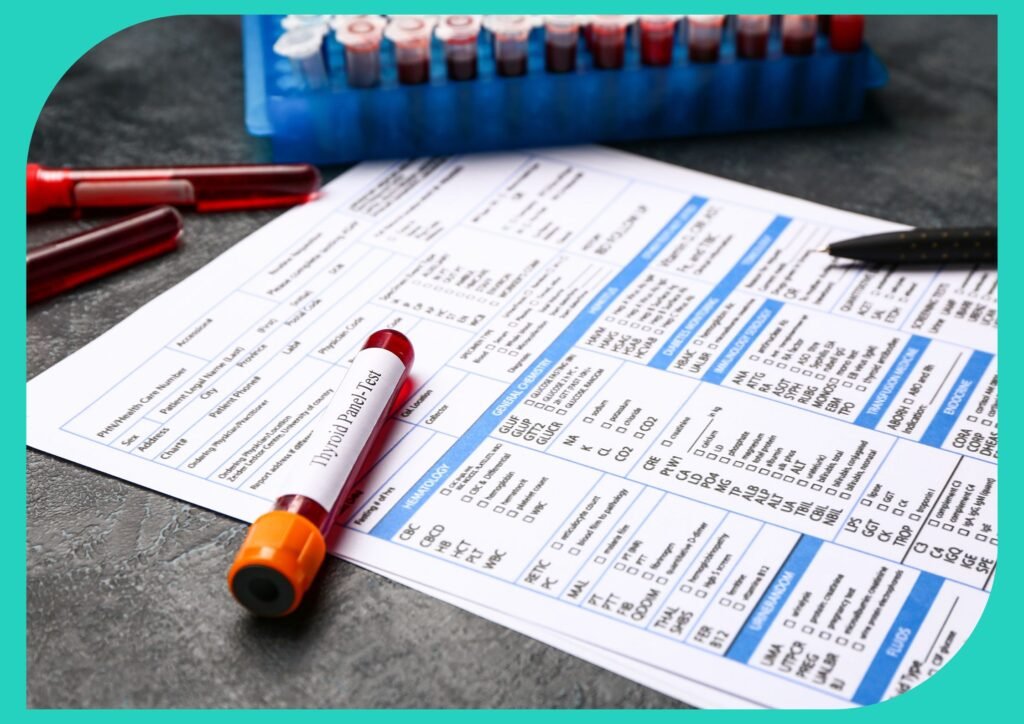
For hyperthyroidism in aging, the diagnosis begins with a thorough evaluation of symptoms. Common symptoms such as weight loss, increased appetite, rapid heartbeat, trembling hands, excessive sweating, fatigue, anxiety, and irritability are taken into consideration.
A physical examination may be conducted to assess any visible signs, such as an enlarged thyroid gland or eye changes in the case of Graves’ disease.
Blood tests are important for diagnosing hyperthyroidism in aging, measuring levels of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). High hormone levels and low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) suggest an overactive thyroid. These tests offer insights into thyroid function and help confirm the diagnosis.
In some cases, additional imaging tests or a thyroid scan may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism.
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or radioactive iodine uptake scan, allow healthcare professionals to visualize the thyroid gland and assess its structure, size, and any abnormalities.
These tests aid in identifying conditions like thyroid nodules or inflammation that may contribute to the hyperactive thyroid.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Effectively managing hyperthyroidism in aging individuals revolves around the goal of restoring balance to thyroid hormone levels and alleviating the accompanying symptoms. Fortunately, a range of treatment options exists to tackle this condition head-on and improve the overall well-being of those affected.
Anti-Thyroid Drugs
One primary approach involves the use of medications. Anti-thyroid drugs work to inhibit the production of thyroid hormones, effectively curbing their excessive release into the body. It is important to consult your doctor for a prescription for these medications.
These medications can help bring hormone levels back within a normal range, providing relief from symptoms and preventing further complications. Regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential while on medication to ensure optimal dosage and efficacy.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine therapy is a potential treatment option. It utilizes a radioactive form of iodine to selectively target and destroy overactive thyroid cells, effectively reducing hormone production and restoring balance.
This treatment is generally safe and well-tolerated, often resulting in long-term improvement in thyroid function. However, it may take weeks or months to see the full effects of the therapy.
Surgery
Surgery may be recommended to manage hyperthyroidism in aging. Thyroidectomy, the removal of all or a portion of the thyroid gland, can permanently eliminate hormone overproduction.
This option is for individuals who cannot tolerate or do not respond well to medications or radioactive iodine therapy. Surgery requires careful consideration and discussion with a healthcare professional, as it carries risks and may require lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers, such as propranolol or atenolol, are often prescribed to manage the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism in aging. These medications help relieve rapid heartbeat, tremors, anxiety, and other related symptoms.
It is crucial for aging individuals with hyperthyroidism to consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment option based on their individual health needs and preferences.
Treatment options for hyperthyroidism depend on factors such as the individual’s health, the severity of the condition, and personal preferences. Healthcare providers collaborate closely with older individuals to identify the most appropriate treatment method, considering their unique circumstances and goals.
Managing hyperthyroidism requires regular follow-up visits, medication adjustments, and thyroid hormone level monitoring. By actively participating in treatment and collaborating with healthcare professionals, older individuals can effectively manage their condition, restore hormone balance, and alleviate symptoms, resulting in an improved quality of life.

Lifestyle Modifications to Manage Hyperthyroidism
In addition to medical interventions, incorporating certain lifestyle modifications is crucial for effectively managing hyperthyroidism. One key aspect is adopting a balanced and nutritious diet that supports thyroid health.
This requires avoiding consuming higher-iodine foods. Stress reduction techniques, such as practising mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies, can also play a pivotal role in managing hyperthyroidism.
Regular exercise, tailored to individual capabilities, not only promotes overall well-being but also helps regulate hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. Prioritizing adequate rest and quality sleep further supports the body’s healing process.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is paramount to devising a personalized plan that aligns with specific needs, ensuring a comprehensive approach to managing hyperthyroidism.
Conclusion
Hyperthyroidism in aging individuals requires careful attention and prompt medical intervention. Identifying the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment options are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
By understanding the signs, exploring treatment options, and adopting management strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling and healthy life while living with hyperthyroidism.
And don’t forget that seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is essential in order to create a customized plan that caters to individual requirements, guaranteeing a well-rounded approach to effectively managing hyperthyroidism in aging.
Disclaimer
The content provided on MySeniors.World is for informational purposes only and is not intended as either financial or medical advice. Always consult a qualified professional before making any investment or health-related decisions.
Posts may contain affiliate links, meaning we earn a commission – at no additional cost to you, if you click through and make a purchase. Your support helps us continue providing valuable content.



















